PROCEDURES
Procedures performed/available include:
A colonoscopy is a procedure used to look for changes — such as polyps or cancer — in the large intestine (colon) and rectum.
During a colonoscopy, a long, flexible tube (colonoscope) is inserted into the rectum. A tiny video camera at the tip of the tube allows the doctor to view the inside of the entire colon.
If necessary, polyps or other types of abnormal tissue can be removed through the scope during a colonoscopy. Tissue samples (biopsies) can be taken during a colonoscopy as well.
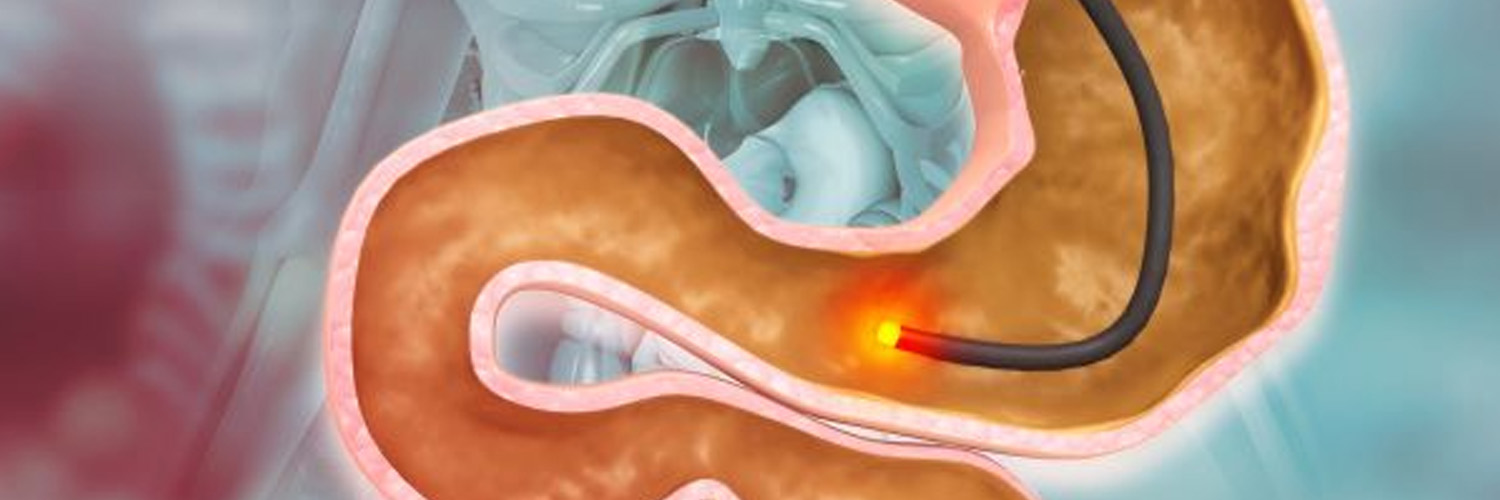
A gastroscopy is a test to check inside your throat, food pipe (oesophagus) and stomach, known as the upper part of your digestive system.
A long, thin, flexible tube with a small camera inside it is passed into your mouth then down your throat and into your stomach.
A gastroscopy can also be used to take tissue samples (biopsies) and treat some conditions such as stomach ulcers or oesophageal strictures.

A transnasal endoscopy (TNE) looks at the foodpipe (oesophagus), stomach and small intestine. A thin flexible tube called an endoscope is passed through your nose and down the back of your throat.
It’s possible to take a small tissue sample (biopsies) through the endoscope for review in the laboratory if this is needed.
Small bowel capsule endoscopy is a minimally invasive test which allows an internal examination of the lining of your small bowel (intestine). It is a capsule containing a small camera which is swallowed by the patient and will move naturally through the digestive tract. As the capsule passes through it will transmit images of the lining of the small bowel. The capsule is disposable and will pass out of the body over the following few days. The capsule which is a similar size to a large vitamin pill (26 x 11 mm) is swallowed easily by most patients.

Large bowel capsule is a test that allows an internal examination of the lining of your large bowel (intestine). It is particularly useful in detecting sources of internal bleeding within the large bowel that may cause symptoms such as anaemia or blood in the motions. The colon capsule is an easy to swallow pill with two cameras inside. It provides clear images and can detect polyps in the large bowel which can progress to colon cancer. The colon capsule does not require sedation or a stay in hospital, and it can help determine if a colonoscopy is necessary. A capsule containing a small camera is swallowed by the patient. As the capsule passes through, it will transmit visual images of the lining of the large bowel.
Double balloon enteroscopy (DBE) is an advanced endoscopic procedure which allows examination of the entire small bowel in real time without invasive surgical intervention.  The procedure can be performed from either end of the digestive tract (mouth or rectum) and can allow further evaluation and/or treatment of abnormalities detected at imaging studies of the small bowel or at small bowel capsule endoscopy.
The procedure can be performed from either end of the digestive tract (mouth or rectum) and can allow further evaluation and/or treatment of abnormalities detected at imaging studies of the small bowel or at small bowel capsule endoscopy.
Double balloon enteroscopy involves inserting a flexible, high-resolution video endoscope into either the mouth or rectum and feeding it along the digestive tract to the small intestine. Two balloons are fixed to the equipment: one to the end of the enteroscope camera, and the other to the overtube. These balloons can be inflated and deflated by a pressure controlled pump.
By inflating and deflating the balloons in an alternating pattern, the enteroscope is able to pass along the whole of the small intestine, visualising it in its entirety. It also allows for biopsies to be taken, or even certain treatments, such as removal of polyps, to be performed.
Removal of polyps by polypectomy and endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR), balloon dilatation, clipping, argon plasma coagulation, tattooing
